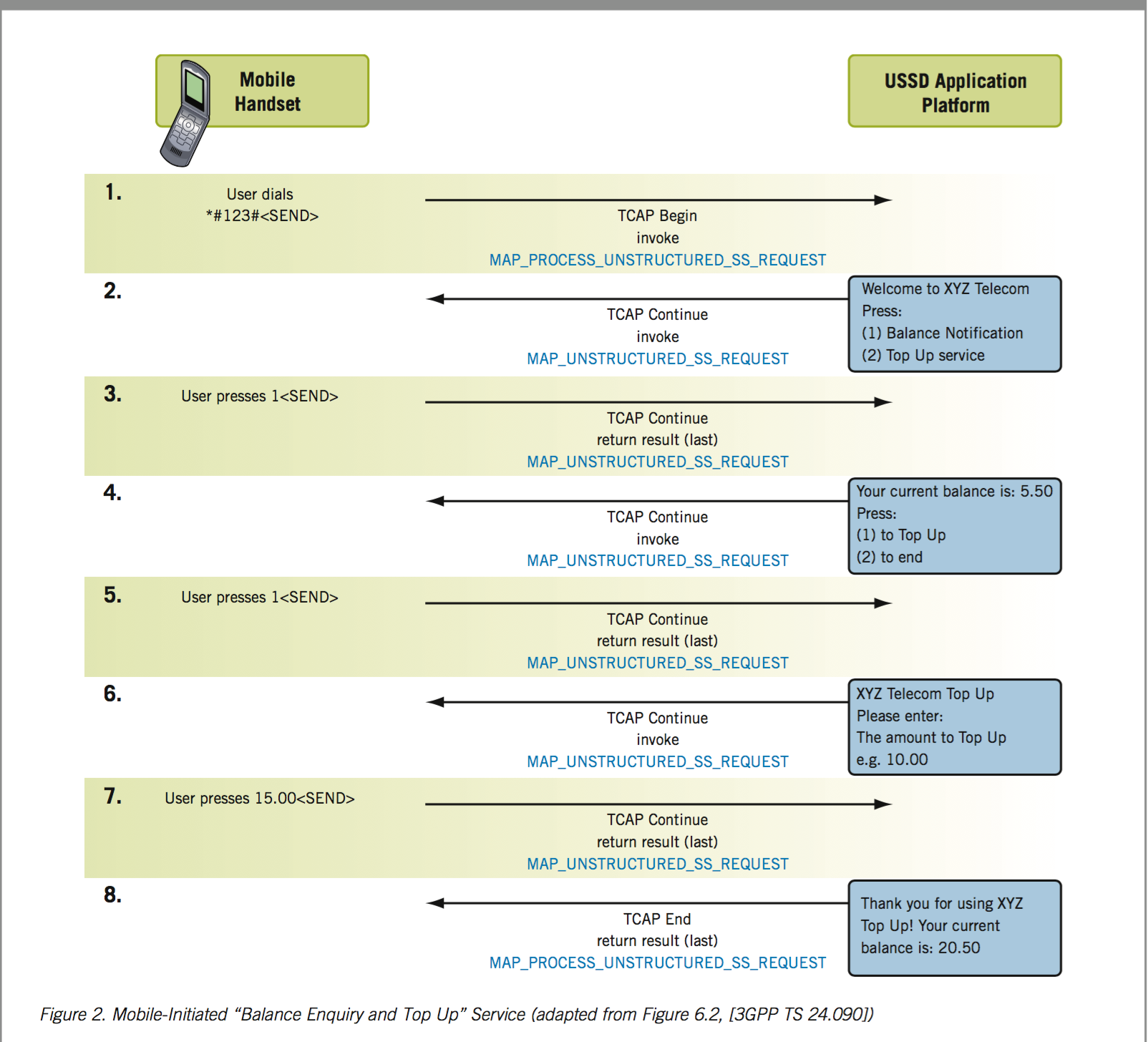
How ussd works¶
Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) is a protocol used by GSM cellphones to communicate with their service provider’s computers. USSD can be used for WAP browsing, prepaid callback service, mobile money services, location-based content services, menu-based information services, or even as part of configuring the phone on the network.
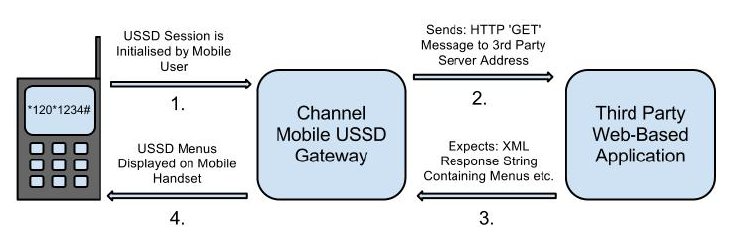
From the diagram above, a request is sent from a mobile phone to a telecom network such Vodafone.
The Ussd Gateway (telecom) then sends the request to your ussd application (i.e where we have the business logic which determines the menu to serve the use on receiving user’s request.)
Your ussd application then responds to the request, and Ussd gateway goes ahead and displays your content to the user
Below is a another diagram to help understand the concept

Why Ussd Airflow¶
Before I explain why we need Ussd Airflow lets first look at one example of ussd user case
How ussd airflow comes in¶
As you have seen in the previous section your ussd application is responsible for the content displayed.
Suppose you want to change the wordings in the ussd screen you are displaying to the user,what is involved in most cases or rather all cases is you make a change in your code and deploy, that’s peanuts for most developers
The problem is once you start having many ussd screens and multiple ussd application and many requirements of changing ussd screen, the task that was peanuts becomes overwhelming and would probably start thinking of a way the Product owners would change the ussd content without you being involved and thats where ussd aiflow comes in, providing an interface for users to change ussd workflows without code change